Suppose you are running a video streaming service. You want to provide the highest quality of experience to your viewers so that they are satisfied with your service and remain regular consumers of your content. Then, every detail of the video streaming process should be well thought through.
One of the essential processes is ensuring that users with any device can access your OTT/IPTV service to watch videos without any issues. The transcoding process gives you a helping hand here. Let’s talk about it in detail.
What is Transcoding?
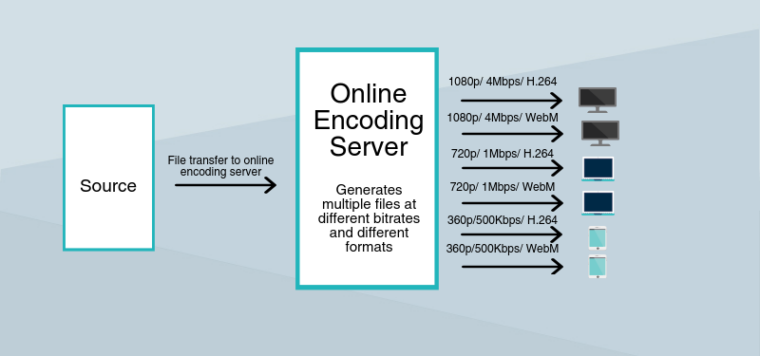
First, we need to cover what happens before transcoding. When you create a video, you have a RAW video file, which is not suitable for delivery via the Internet. It should go through the encoding process in the first place.
An encoder converts a video into an IP stream. The encoder compresses the information so that it takes less storage space.
Then, the transcoding process is essential as it makes the video suitable for playback on any platform and device, especially when it doesn’t support the current video format or has limited storage capacity.
For example, some devices might require a lower-resolution stream. The high-resolution video is transcoded into a lower-resolution video. As a result, a user receives a smooth playback.
What Factors Influence Video Transcoding?
There are multiple factors that influence the video transcoding process. For example, resolutions, bitrates, codecs, frame rates, and others – these elements impact the transcoder’s speed, quality, cost, and size.
You should determine the resolution: whether 1902×1080, 1280×720, or any other is necessary for the receiving device. Then, the bitrate should be defined. And finally, choose the codec: H.264, H.265, VP9, or AV1.
What are the Types of Video Transcoding?

There are three types of video transcoding:
- Lossy-to-lossy means that your video file is already of poor quality, and transcoding will only make it worse. This type of video transcoding can be used to lower the bitrate and save storage space.
- Lossless-to-lossless transcoding allows compressing a file losslessly. It is useful for changing media to new formats without losing quality.
- Lossless-to-lossy allows less quality loss than the first transcoding type and creates file sizes suitable for portable devices.
Why is Video Transcoding Vital?
Content providers want to ensure a great experience quality for their viewers. But it is not as simple as it may seem. The provider, at least, needs to make sure that the video is encoded and streamed to all devices.
Video transcoding helps create multiple bitrates for adaptive bitrate streaming (ABS). It means that a video should have many versions for successful video delivery using ABS.
Video transcoding keeps the viewing experience buffer-free as there are multiple versions of the video with various bitrates and resolutions. If bandwidth changes, a video player will switch to a suitable rendition.
Reducing the size of video files allows using fewer resources, such as battery power or storage space.
Most importantly, as different devices support different codecs, transcoding allows providers to reach as many devices as possible. As a result, you have more satisfied viewers and regular customers.

Drawing the Line
Transcoding is a vital process for providing the highest quality of experience to viewers. It allows you to reach more devices by creating multiple versions of the same video so that any device can play it smoothly.
The result is a happy customer who returns for more content on your video streaming service. You have regular viewers and a stable revenue stream.
